Stats How to Pick Which T Value to Use
T is the t-statistic. For example the shaded region represents the probability of obtaining a t-value of 28 or greater.

Using The Hhmi Mathematics And Statistics In Biology Guide In The Classroom Biology Statistics Math Statistics
For a statistical test to be valid your sample size needs to be large enough to approximate the true distribution of the population being studied.

. You can compare your calculated t-value against the values in a critical value chart to determine whether your t-value is greater than what would be expected by chance. When performing a t-test we compare sample means by calculating a t-value also called a t-statistic. First enter the value for the Degrees of Freedom.
Our t-value of 2 indicates a positive difference between our sample data and the null hypothesis. For example if you want a t-value for a 90 confidence interval when you have 9 degrees of freedom go to the bottom of the table find the column for 90 and intersect it with the row for df 9. Whether your data meets certain assumptions.
Hence we can see that how large or how small the T statistic is depends on how close or far away the sample mean is from the hypothesised mean. If a t-value is sufficiently improbable when the null hypothesis is true you can reject the null hypothesis. Using the previous example alpha value of 005 complete the formula to find the critical probability.
As is seen in the wikipedia link this is performed by calculating the t value using the formula. The number you see is the critical value or the t-value for your confidence interval. The critical value is the value in the table that aligns with a two-tailed value of 005 and a degrees of freedom of 22.
In statistics model selection is a process researchers use to compare the relative value of different statistical models and determine which one is the best fit for the observed data. After entering these values the T score calculator will generate the T value right-tailed and the T value two-tailed. T statistic formula or T Score formula.
X1 is the mean value for sample 1. Critical probability p 1 - 005 2 1 - 0025 0975. Our t-value of 2 is an unusual value but we dont know exactly how unusual.
To use the t-distribution table you only need to know three values. Ttest write read paired TRUE Paired t-test data. Using the alpha value from the first formula calculate the critical probability.
The critical probability in this example is. Around 68 of values are within 1 standard deviation of the mean. All these test statistics are ratios which helps you understand their null values.
The degrees of freedom of the t-test. T values P values and poker hands. Here is a road map.
The critical value that most statisticians choose is 005. Around 997 of values are within 3 standard deviations of the mean. When a t-value equals 0 it indicates that your sample data match the null hypothesis exactly.
The graph shows that there is a reasonable probability of obtaining a t-value from -2 to 2 when the null hypothesis is true. Around 95 of values are within 2 standard deviations of the mean. This will be the critical value which you can then express as a t statistic or a Z-score.
T values of larger magnitudes either negative or positive are less likely. The number of tails of the t-test one-tailed or two-tailed The alpha level of the t-test common choices are 001 005 and 010. If so you can reject the null.
Heres the formula for a two-sample t-test. The types of variables that youre dealing with. To determine which statistical test to use you need to know.
Thus you should only decide based upon whether the sample size is below 30. The t-score which generates a p-value below your threshold for statistical significance is known as the critical value of t or t. In the context of how t-tests work you assess the likelihood of a t-value using the t-distribution.
The far left and right tails of the distribution curve represent instances of obtaining extreme values of t far from 0. N1 is the number of people from the 1st sample who provided a response to the survey. If the sample mean is close to hypothesised mean we will get a T statistic close to zero.
Since out test statistic t 134 is smaller. This value should be between 0 and 1 only. Tfracbarx-mussqrtn where barx is the sample mean ie the mean of the dependent variables measured values mu is the population mean s is the standard deviation of the sample and n is the sample size.
True difference in means is not equal to 0 95 percent confidence interval. Our ultimate goal is to determine whether our t-value is unusual enough. This number turns out to be 2074.
T-Tests Null 0. For a 1-sample t-test when the sample mean equals the hypothesized mean the numerator is zero which causes the entire t-value ratio to equal zero. X2 is the mean value for sample 2.
Write and read t 0867 df 199 p-value 03868 alternative hypothesis. The empirical rule or the 68-95-997 rule tells you where most of the values lie in a normal distribution. This gives you a t-value of 1833 rounded.
I performed this calculation and calculated that the t_value is equal to npaveragev1 - v2 npsqrtlenv1 npstdv1 - v2 -16061552162815307 However using the scipystats package I get a slightly different result. AIC weights the ability of the model to predict the observed data against. A larger t-value shows that the difference between group means is greater than the pooled standard error indicating a more significant difference between the groups.
In this case both problems have known population mean and standard deviation. -0694 1784 sample estimates. The first approach we can use to determine if our results are statistically significant is to compare the test statistic t of 134 to the critical value in the t distribution table.
The 1st problem has n30 so you should use z-table. Then enter the value for the Significance level. This 005 means that if we run the experiment 100 times 5 of the times we will be able to reject the null hypothesis and 95 we will not.
T statistic Sample mean hypothesised meansample standard error. T-scores are used when the conversion is made without knowledge of the population standard deviation and mean. Where mu_0 is set to 0.
Because Im showing the results of a two-tailed test well use the t-values of 2 and -2. This means that the difference in group means is 1279 standard deviations away from the mean of the distribution of the null. I have two crucial points to explain before we calculate the probability linked to our t-value of 2.
Example of a p-value The two-tailed t-test of the difference in test scores generates a t-value of 1279. The Akaike information criterion is one of the most common methods of model selection. N2 is the number of people from the 2nd sample who provided a response to the survey.

Simple Guide For Selecting Statistical Tests When Comparing Groups Data Science Central Data Science Statistical The Selection

Comparing Groups For Statistical Differences How To Choose The Right Statistical Test Data Science Learning Statistics Math Machine Learning Deep Learning

Earth Day Ap Stats Choosing The Right Inference Method Coloring Sheet Video Video Inference Ap Statistics Method
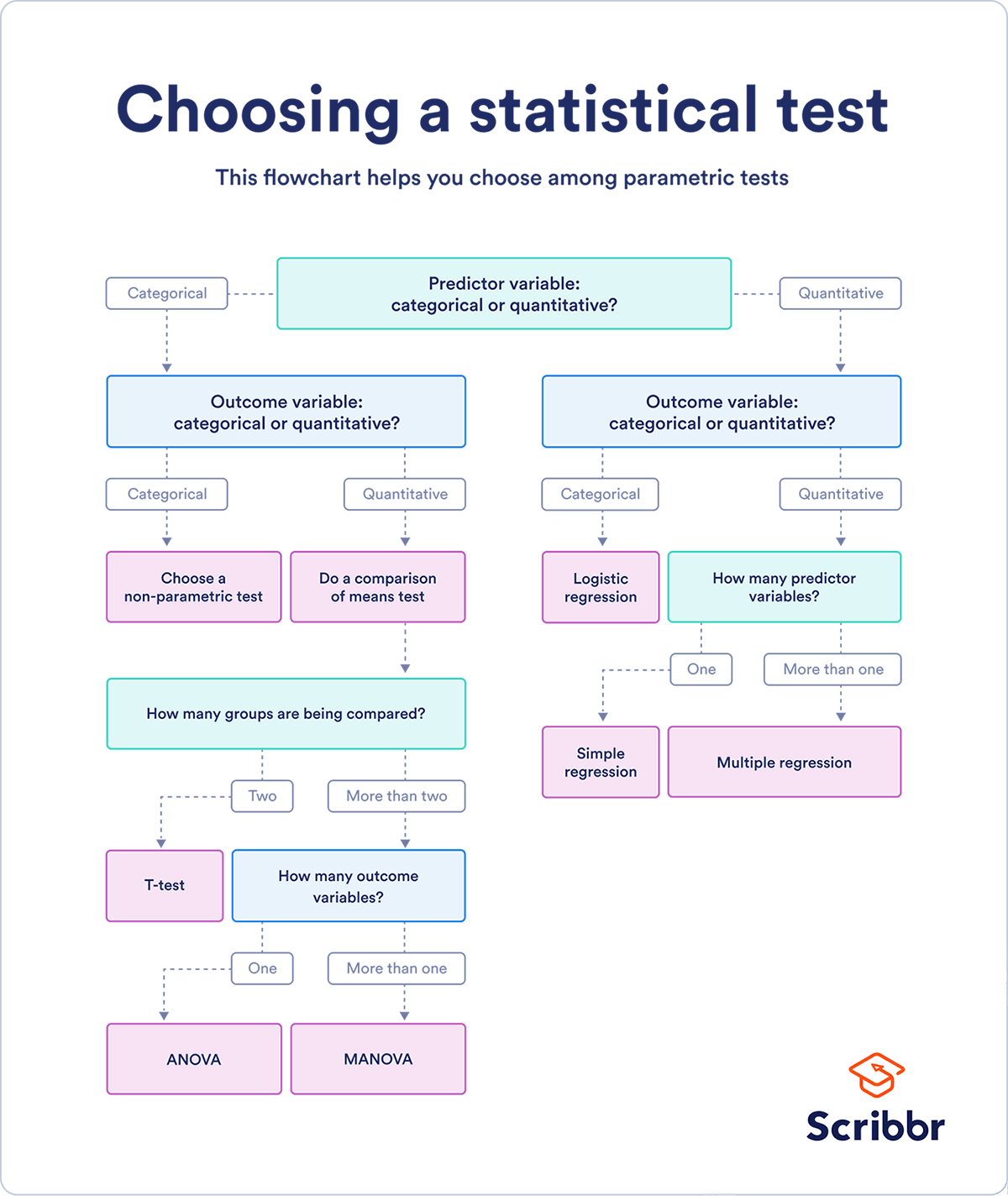
Choosing The Right Statistical Test Types And Examples

Flow Chart For Selecting Commonly Used Statistical Tests Statistics Math Data Science Learning Research Methods

When Dealing With Normally Distributed Data It Is Crucial For Lean Six Sigma Practitioners To Be Able To Co Data Science Learning Statistics Math Data Science

Statistics Assignment Homework Help Statistics Math Data Science Learning Statistics

Are Any Of These A Mark On You Avoid Being A Statistic By Recognizing And Correcting Today Small Business Resources Small Business Tips Business

Http Abacus Bates Edu Ganderso Biology Resources Stats Flow Chart V2014 Gif Statistics Math Research Methods Data Science

Hypothesis Testing Cheat Sheet Fairly Nerdy Statistics Math Data Science Learning Statistics Cheat Sheet

Statistical Testing Flowcharts Data Science Learning Data Science Statistics Data Science

Inferential Statistics Types Of Calculations Definition And Examples Data Science Data Science Statistics Statistics Math
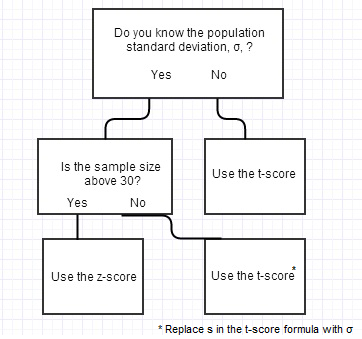
T Score Vs Z Score What S The Difference Statistics How To

An Intuitive Guide To Various Statistical Tests Decision Tree Data Science Learning Statistics Math

Hypothesis Testing Decision Tree Statistics Math Data Science Learning Math Methods

Statistical Inference Which Tests To Perform Inference Science Student Hypothesis



Comments
Post a Comment